|
Childhood is a time of rapid change. Some of these changes are obvious, such as height gain, language ability and physical dexterity. Others are less obvious, such as how children make sense of the information in their environment. To understand the rapid changes of childhood, children’s abilities are often judged against developmental milestones, such as acquiring language (babbling, talking), cognition (thinking, reasoning, problem solving), motor coordination (crawling, walking) and social skills (identity, friendships, attachments). But how does digital technology influence the acquisition of these important skills? Does technology hinder a child’s physical, social and cognitive development, or does it provide exciting opportunities for learning?
The entertainment and interactivity of tablets and smartphones has made them attractive to children. Touch-screen interfaces mean that digital technologies are now accessible for children at a very young age. But do children find digital technologies exciting for reasons beyond simple entertainment? The amount of digital technology available to my young daughters is massively different to that in my own childhood. As both a parent and a Social Worker, I've found it difficult to make sense of media reports and research findings in this controversial area. Is technology beneficial or detrimental to child development? Does screen time lead to increased distractibility, obesity and loneliness? Or does it offer opportunities for autonomy and experimentation beyond anything imagined when I was a young child? As the generation gap widens between adults and children’s' understanding of new technologies, how will we protect them from the risks while allowing them to benefit from the opportunities new technologies offer? In 2014 both Ofcom and the NSPCC (Jütte et al.) found that one in three children owned their own tablet. Figures published by the NSPCC also show smartphone ownership increasing with age (20 per cent of 8–11-year-olds and 65 per cent of 12–15-year-olds). These profound changes are reshaping children’s digital environment. The recent EU Kids Online Network project, called Zero to Eight, illustrates just how pervasive technology is becoming for younger children. The project report identified a significant increase over the previous five years of children under nine years old using the internet (Holloway et al., 2013). In particular it noted a growing trend for very young children (pre-schoolers) to use tablets and smartphones to access the internet:
Whilst children are now going online at a younger age, their ‘lack of technical, critical and social skills may pose [a greater] risk’ (Livingstone et al., 2011). The challenge for parents is how best to manage the risks alongside the benefits. I’ll get back to this later…
Children and Digital Technologies Children are often very engaged by digital technology. But why is it so compelling for young children to spend so much time interacting with their digital world? Firstly, technology is fun. Child-centred technology in particular is especially designed to be as entertaining and captivating as possible. Similarly, a big attraction of technology for children is that they see their parents and peers using it, and a major part of childhood is ‘modelling’ the behaviour of those around them, particularly parents: that is, children learn from observing and imitating others around them. Richard Ryan and Edward Deci’s (2000) self-determination theory (SDT) seems particularly relevant to untangling the reasons behind young children’s fascination with the digital world. According to SDT, there are two overarching types of motivation, ‘intrinsic motivation’ and ‘extrinsic motivation’. The former refers to doing an activity for its own sake because it is enjoyable and this is thought to lead to persistence, good performance and overall satisfaction in carrying out activities. Ryan and Deci outline three basic psychological needs associated with intrinsic motivation that can be applied to children’s use of technology:
Although each of these three basic psychological needs may not be met for every child, the self-determination theory offers a good psychological basis for understanding children’s intrinsic motivation in using technology. According to one study, children are currently spending more time with technology than they do in school or with their families. Similarly, children as young as 2, 3 and 4 are playing with their parents’ phones or tablet devices; and some psychologists argue that this has an enormous impact on their brain development, as well as on their social, emotional and cognitive skills. This raises an important question: in this 24/7 digital world, should parents be setting new rules for their children’s engagement with technology? Should we be promoting new parenting classes for the modern age? Generational Divide The idea of a generational divide between children and adults has been a popular topic among psychologists and sociologists. This has resulted in the use of labels such as the ‘digital native’, the ‘net generation’, the ‘Google generation’ or the ‘millenials’, each of which highlights the importance of new technologies in defining the lives of young people. The most contentious term is the ‘digital native’. The term first appeared in an article by Marc Prensky to describe those children who spend much of their lives ‘online’, constantly ‘switched on’. It represents ‘native speakers’ who are ‘fluent in the digital language of computers, video games and the Internet’. There is a distinction between ‘digital natives’, who are those generally born after the 1980s and are technologically adept and comfortable in a world of technology, and ‘digital immigrants’, who are generally born before the 1980s and are fearful or less confident in using technology. To justify his claims Prensky draws on the widely held theory of neuroplasticity. This means that our brains are highly flexible and subject to change throughout life. The different neural connections in the brain change and evolve throughout childhood in response to the environment. It is claimed that young children’s brains now are developing differently to the way adults’ brains have developed, as children are growing up surrounded by new technologies. This topic of neuroplasticity is something that I have also covered in Risk, Resilience and Adoption. Safeguarding Many parents, teachers and Social Workers have legitimate reasons to worry about children’s engagement with the digital world. We know that children are likely to run risks if they access the internet unsupervised, or stay online for long periods of unbroken time. Examples of the apparent risks appear in the work of Howard-Jones, who analysed current research in neuroscience and psychology. He states that the developing brain can be susceptible to environmental influence, and digital technology opens it to risks including:
You can also find research into internet addiction, aggressive game-playing, grooming and bullying, which have also been linked to children’s exposure to the digital world. Social Media can also present problematic situations for adopted children, and those in foster placements or subject to child protection plans. Even the Pope waded in on the debate earlier this month, warning parents not to let children use computers in their bedrooms because of the 'dirty content' on the internet. Whether you are a digital optimist or pessimist, it’s obvious that while technology brings about opportunities, it also has associated risks. This has led to some professionals arguing that parents should limit young children’s use of, and exposure to, new digital technologies. But is this really the answer? Is simply restricting children’s access actually the best way to ensure their safety? Restricting access to technology may also restrict opportunities for children to develop resilience against future harm and I would argue that simply restricting access or removing technology from children’s lives seems inappropriate (except as a short term measure in cases where technology is presenting a significant risk of harm to the child). Perhaps we need to review parenting methods so we ensure sufficient levels of support for children growing up in this highly digital modern world. If we look at self-determination theory, the idea of giving children autonomy and choice to make appropriate decisions about their own digital world could be the answer. According to some, we need to trust in the maturity and judgement of children. We have to be able to trust their social skills in successfully negotiating these new ways of behaving and successfully managing or avoiding risks (Banyard and Underwood, 2012). It is important to recognise that children’s perceptions of problematic online situations may differ greatly from those of adults. Because of the different perceptions of adults and young people, and the lack of a neat distinction between positive and negative experiences online, many professionals opt to avoid the term ‘risk’, and prefer to talk about ‘problematic situations’. Research by Vandoninck and colleagues, based within the UK, tackles the idea of giving children autonomy to make their own choices. Awareness of online risks motivates children to concentrate on how to avoid problematic situations online, or prevent them from (re)occurring. This brings me to the concept of preventive measures – what children actually do or consider doing in order to avoid unpleasant or problematic situations online. Vandoninck and colleagues identified five main categories of measures discussed in the literature:
Perhaps the key focus of parents and professionals should be on helping children to acquire the knowledge and skills to moderate their own online behaviours; to develop resilience to risks and to become responsible digital citizens of the twenty-first century (Banyard and Underwood, 2012). For more information about safeguarding, take a look at my other posts on online safety and follow me on facebook and twitter.
0 Comments
I've written a couple of posts recently about Protecting Young Children Online and Protecting Big Kids Online. I was thrilled at how many times they were viewed and shared (Thank you!) and I hope they have helped you to feel more confident in safeguarding your children in the digital age. Since I last posted I've found the new Fire HD Kids Edition. It has some great easy-to-use parental controls where you're able to manage usage limits, content access and educational goals, plus there's a 2 year worry free guarantee! It looks fab! Children’s apps and websites were in the news on privacy grounds earlier this week, after the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) announced a review of how these services collect data on their young users. It will form part of an international project, coordinated by the Global Privacy Enforcement Network, and will look at 50 websites and apps, particularly what information they collect from children, how that is explained, and what parental permission is sought. The websites and apps will include those specifically targeted at children, as well as those frequently used by them. So how can parents decide which sites, apps and games are appropriate? Today I was emailed about the NSPCC's updated Net Aware guide which helps parents to understand what their children are doing online and hopefully maintain open channels of communication. It's a huge database providing information on sites, apps and games. It tells you what it is, why kids like it and provides an age rating to help parents judge whether it's appropriate for their child. After having a look through the site I realised that I probably haven't heard of half of them before. 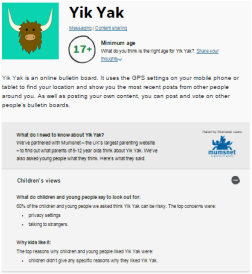 Research by the NSPCC earlier this year found that many parents have gaps in their online knowledge and don't talk about the right issues with their children. For example, Tinder, Facebook Messenger, Yik Yak and Snapchat were all rated as risky by children, with the main worry being talking to strangers. However, for the same sites the majority of parents did not recognise that the sites could enable adults to contact children. Although eight out of ten parents told the NSPCC that they knew what to say to their child to keep them safe online, only 28% had actually mentioned privacy settings to them and just 20% discussed location settings. One of the best ways of safeguarding your child online is to maintain open channels of communication. Here are my top tips:
Take a look at the NSPCC guide and let me know what you think. I was overwhelmed at the positive response I got for my earlier post about Protecting Young Children Online (Thank you for sharing!) so as promised I am following up with one for older children in Key stage 2. The tips below should be used in addition to the security measures outlined last time. Of course, you might want to give them access to a greater range of websites now that they are older; however, you should still ensure that they are age appropriate. Technology and the internet has changed a lot since we were kids and keeping up to date can be a challenge. Many parents feel overwhelmed as their children’s technical skills seem to far exceed their own. However, children and young people still need support and guidance when it comes to managing their lives online if they are to use the internet positively and safely. There are a number of books and online resources available to increase your technical knowledge and skills. If you aren't that confident online or with electronic devices it might be worth brushing up now before the kids really surpass us in their adolescent years. Is your child safe online? A Parents Guide to the internet, facebook, mobile phones & other new media is a great starting point. It covers all forms of new media - iPhones, apps, iPads, twitter, gaming online - as well as social networking sites. If you want to learn more of the techie stuff behind maintaining personal privacy Internet Privacy For Dummies is a really accessible quick reference guide. Topics include securing a PC and Internet connection, knowing the risks of releasing personal information, cutting back on spam and other e–mail nuisances, and dealing with personal privacy away from the computer. The UK Safer Internet Centre offers a Parents' Guide to Technology. It introduces some of the most popular devices, highlighting the safety tools available and empowering parents with the knowledge they need to support their children to use these technologies safely and responsibly. The NSPCC and NetAware have also created a brilliant resource detailing sites, apps and games that they have reviewed. It's a huge database telling you what they are, why kids like them, and it gives an age rating to help you to judge whether it's appropriate for your child. Anyway, back to protecting your big kids... One of the best ways of safeguarding your child online is to maintain open channels of communication.
It’s never too early or late to start talking to your child about staying safe online. There are a number of great resources available for parents and professionals to access and download. On my earlier post I showed you Smartie the Penguin by ChildNet. For children in key stage 2 there’s The Adventures of Kara, Winston and the SMART Crew. It’s a cartoon and each of the 5 chapters illustrates a different e-safety SMART rule.  is for keeping safe. Be careful what personal information you give out to people you don’t know  is for meeting. Be careful when meeting up with people you’ve online chatted to online.  is for accepting. Be careful when accepting attachments and information from people you don’t know they may contain upsetting messages or viruses.  is for reliable. Always check information is from someone reliable and remember some people may not be who they say they are.  is for tell. Always tell a trusted adult if something or someone online is making you worried or upset. You can watch the full movie online or download it to a device for later. For children at the older end of this age group, CBBC has an online comedy drama called Dixi. Dixi both encourages children to enjoy the creativity of the internet while also getting them to think about the potential dangers of social networking, from online privacy and safety settings, to the real-world consequences of cyber bullying. Cheryl Taylor, Controller of CBBC, says: “It’s important to raise awareness about safety online and Dixi does this in an engaging, educational and entertaining way”. There are also games that complement the drama for children to access through their website. You could also sit down together to watch the film below by the Child Exploitation and Online Protection Centre. It’s called 'Jigsaw' and is suitable for this age group. It helps children to understand what constitutes personal information and enables children to understand that they need to be just as protective of their personal information online, as they are in the real world. It also directs them where to go and what to do if they are worried about any of the issues covered. It could be a great conversation starter and open up the channels of communication. I hope that you find this helpful. It can be a little intimidating when our children venture into the virtual world but with support and boundaries they will have have access to a resource with huge educational and social value. I'll post again soon with tips for supporting Teenagers / Young People in the digital age. Please follow me on facebook so that you don't miss it!
A friend asked me about e-safety today. She was concerned after finding her child on an inappropriate website and panicked. Her initial reaction was to revoke all on-line privileges as she did not feel confident in her ability to manage the situation. This is a natural reaction. We often want to remove our children from all situations which might cause them harm but in this day and age, it isn't particularly realistic. Children need to learn how to use computers and the internet. It will play a huge part in their lives growing up and should be supported if they are to enjoy and achieve, make a positive contribution and achieve economic well-being. So, here are my top tips for protecting young children (Foundation and Key Stage 1) whilst on-line. I will write a separate post for older children at a later date.
It's never too early to start talking to your child above staying safe on-line. There are a number of great resources available for parents and professionals to download. One of my current favourites is Smartie the Penguin by ChildNet International. You can download the story from the tools section of this website along with prompts for exploring the themes raised. It is a great way of introducing the boundaries we highlighted earlier in a child centred way.
The story follows Smartie the Penguin as he learns what to do when pop ups appear, when he finds himself on an inappropriate webpage and when he receives a message from a stranger. There are also a number of books that you can share with children to explain the importance of internet safety. Chicken Clicking is described as Little Red Riding Hood for the iPad generation; this is the perfect book for teaching children how to stay safe online. Penguinpig teaches children about stranger danger online. When a little girl reads about a penguinpig on the Internet, she decides that she must go and find one. Not telling her parents, she sets off to the zoo and carefully follows the instructions from the website. Penguinpig has received acclaim from children's authors Andrew Cope and Ian Whybrow, and has been recommended for families and schools by Claude Littner (BBC1's The Apprentice). The Internet is Like a Puddle by Big Hug Books attends to the wonderful aspects of electronic communication as well as gently discusses some of the possible pitfalls of sharing, chatting and using data. The Big Hug books grew out of letters sent to children and their families after their psychology sessions. Each book has its origins in a real need for a real child with a real problem and offers real strategies from a real psychologist. The heart-felt illustrations and simple words aim to simplify tricky situations and soothe strong emotions. The books aim to give children, and the people who care for them, a way to talk about problems. Digiduck's Big Decision is an illustrated children's book that tells the story of Digiduck and his friends, to help children understand how to be good friends to others on the internet. Designed for children age 3-7 years (Foundation stage and KS1) this book is very accessible for this audience. I hope that you find this helpful. It can be a little intimidating when our children venture into the virtual world but with support and boundaries they will have have access to a resource with huge educational and social value. |
AuthorI'm a Qualified Children's Social Worker with a passion for safeguarding and family support in the UK. Archives
August 2016
Categories
All
|









